0989.761.499
0989.761.499 contact@tapchithangmay.vn
contact@tapchithangmay.vn  18/647 Lạc Long Quân, Tây Hồ, Hà Nội
18/647 Lạc Long Quân, Tây Hồ, Hà Nội
Any form of using the content published by Elevator Magazine at www.tapchithangmay.vn must be approved in writing by the Magazine.
© TapchithangmayLicense No: 510/GP-BTTTT dated 06/08/2021
Editorial's Office: 18/647 Lac Long Quan Street, Tay Ho District, Hanoi
Deputy Editor-in-Chief in charge: Trinh Hong Le
Magazine SubscriptionsAny form of using the content published by Elevator Magazine at www.tapchithangmay.vn must be approved in writing by the Magazine.
© Tapchithangmay



















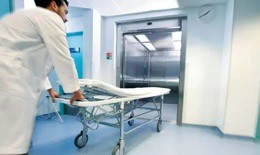
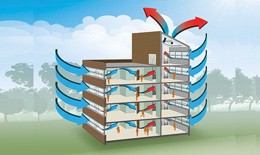
![[Snapshot] Interlift 2025 Officially Opens in Nürnberg, Germany [Snapshot] Interlift 2025 Officially Opens in Nürnberg, Germany](https://media.tapchithangmay.vn/share/web/image/2025/10/IMG_0876_260x155.jpeg)