EM – Elevator test tower is a work to help elevator manufacturers test new elevator technologies and technical conditions for elevator operation before commercialization. With the trend of building higher and higher buildings, the elevator must also have a corresponding travel with higher speed, higher technology, so the requirements for the elevator test tower are also gradually higher over time.
The necessity of the elevator test tower
What is the elevator testing process for? This work is so that experts can detect unexpected problems during elevator operation such as electrical short, equipment not working, circuit conflicts, safety devices not activated, device is not precisely controlled according to the user’s use.
In some cases, the elevator test tower is also used to test the ability to stop the elevator when the cable breaks, to measure the vibration of the elevator when the elevator moves to increase the elevator speed. Check the safety of the safety devices on the elevator.
In particular, companies specializing in the production of elevators for super-high-rise buildings have invested in building super-tall test towers. The test tower must have the necessary height to measure and test the high speed of high-tech elevators for super-tall buildings. The current highest elevator speed is about 20 m/s. The tower also needs a minimum height to measure the force exerted on the cables and the strength of the cables for super high-rise buildings. Because in addition to bearing the impact of the cabin, the counterweight, the traction cable must also bear its own gravity.
Elevator towers are typically around 100 meters high, but the increasing construction of skyscrapers around the world has created a need for much taller test facilities. In Vietnam, only very few elevator test towers have been built. In particular, at the end of 2019, Thien Nam Elevator Joint Stock Company held the opening of the first elevator safety test tower in Vietnam located at its factory in Long An.
The tower has a height of 32m, equivalent to a 10-storey building, with 4 simulated floors with an investment of more than 3 billion VND. This will be a place for testing and safety inspection of all elevator lines manufactured by Thien Nam before being shipped to the market.
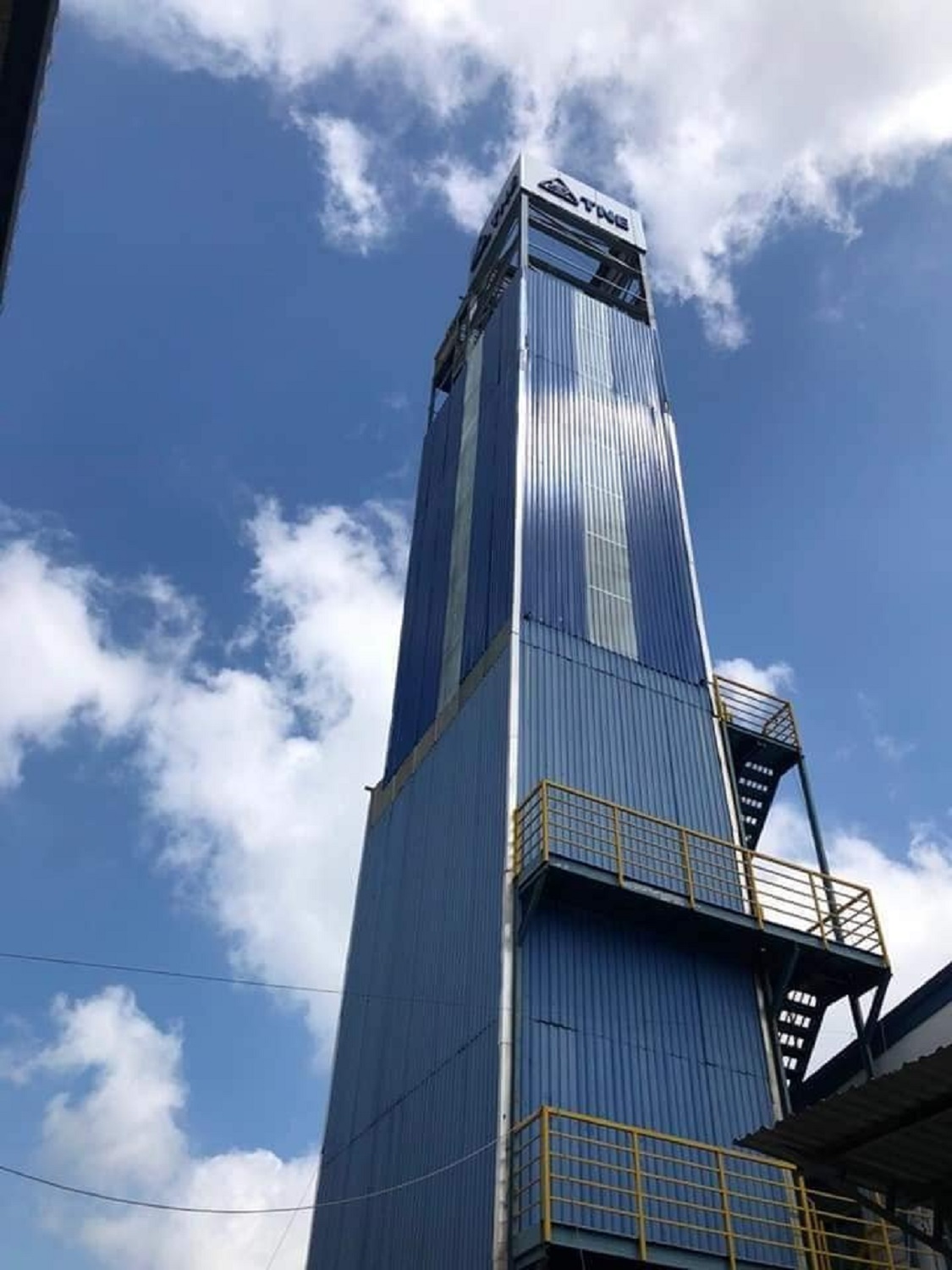

TNE’s elevator test tower
In fact, there are no specific regulations on standards and regulations for elevator test towers, but Vietnam Standard TCVN 6396-50:2017 (equivalent to EN 81-50:2014) and some other documents The specific regulation “Safety requirements for elevator construction and installation – Inspection and testing”, including requirements for design, calculation, inspection and testing of elevator parts… It is important that in order to inspect and test according to the requirements specified in TCVN 6396-50:2017, it is necessary to build specialized test towers and meet the test requirements. Especially, pre-inspection before circulation for imported elevators and domestically produced elevators to ensure safety.
The tallest elevator towers in the world
The world’s tallest test towers today are built by some of the world’s major elevator manufacturers to test new designs, new technologies or new materials. As can be seen from the list, the majority of these test towers are located in Asia and their height has steadily increased over the years.
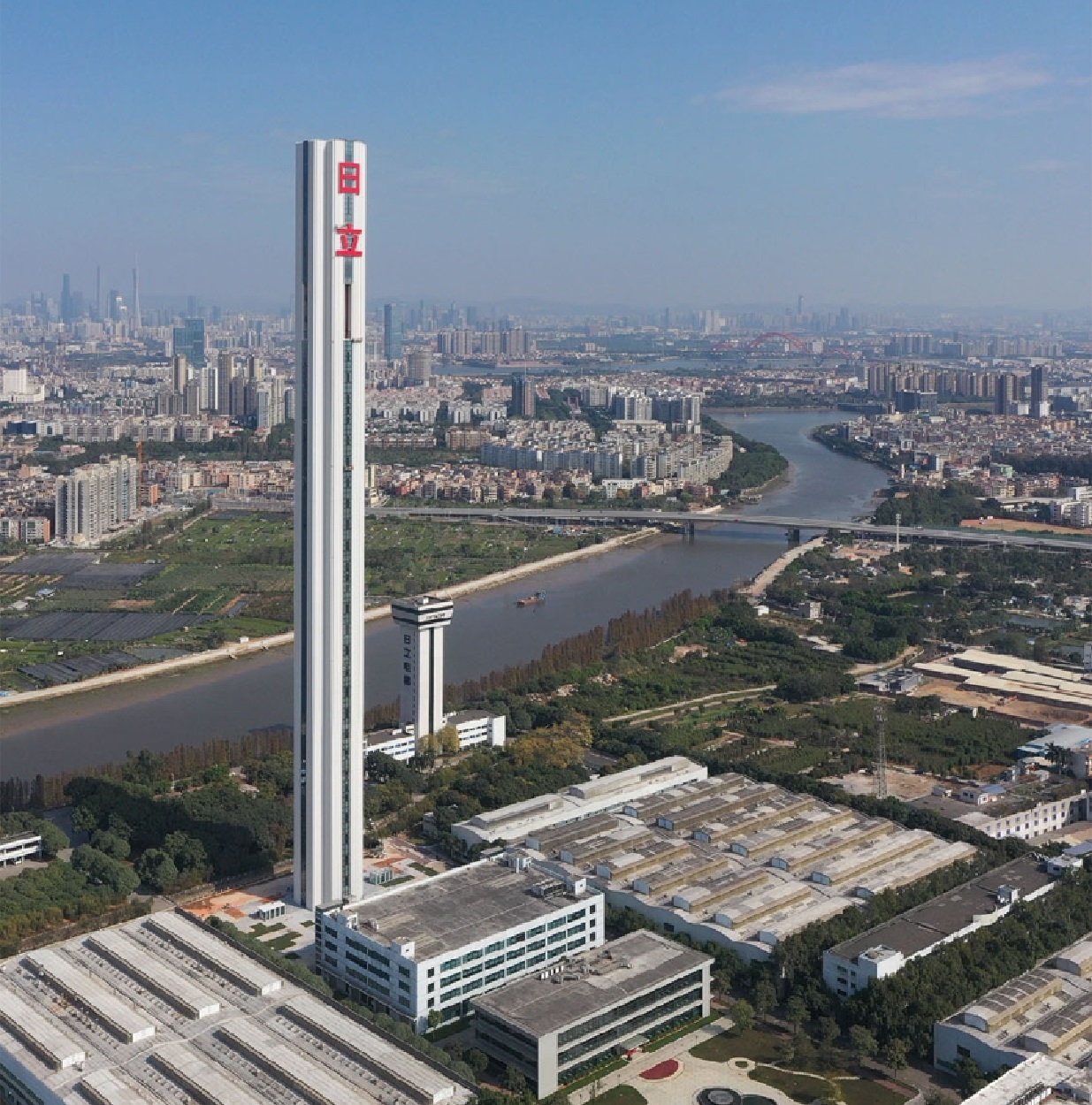

Tower H1 – Guangzhou, China : 273.8 m
Tower H1 is owned by Hitachi. With a height of 273.8 m, this is the world’s tallest elevator test tower today when completed in January 2020. Including the 15 m (49 ft) deep basement, the tower’s overall height is 288.8 m (948 ft). The structure includes 15 elevator test shafts, total length 2.2 km.
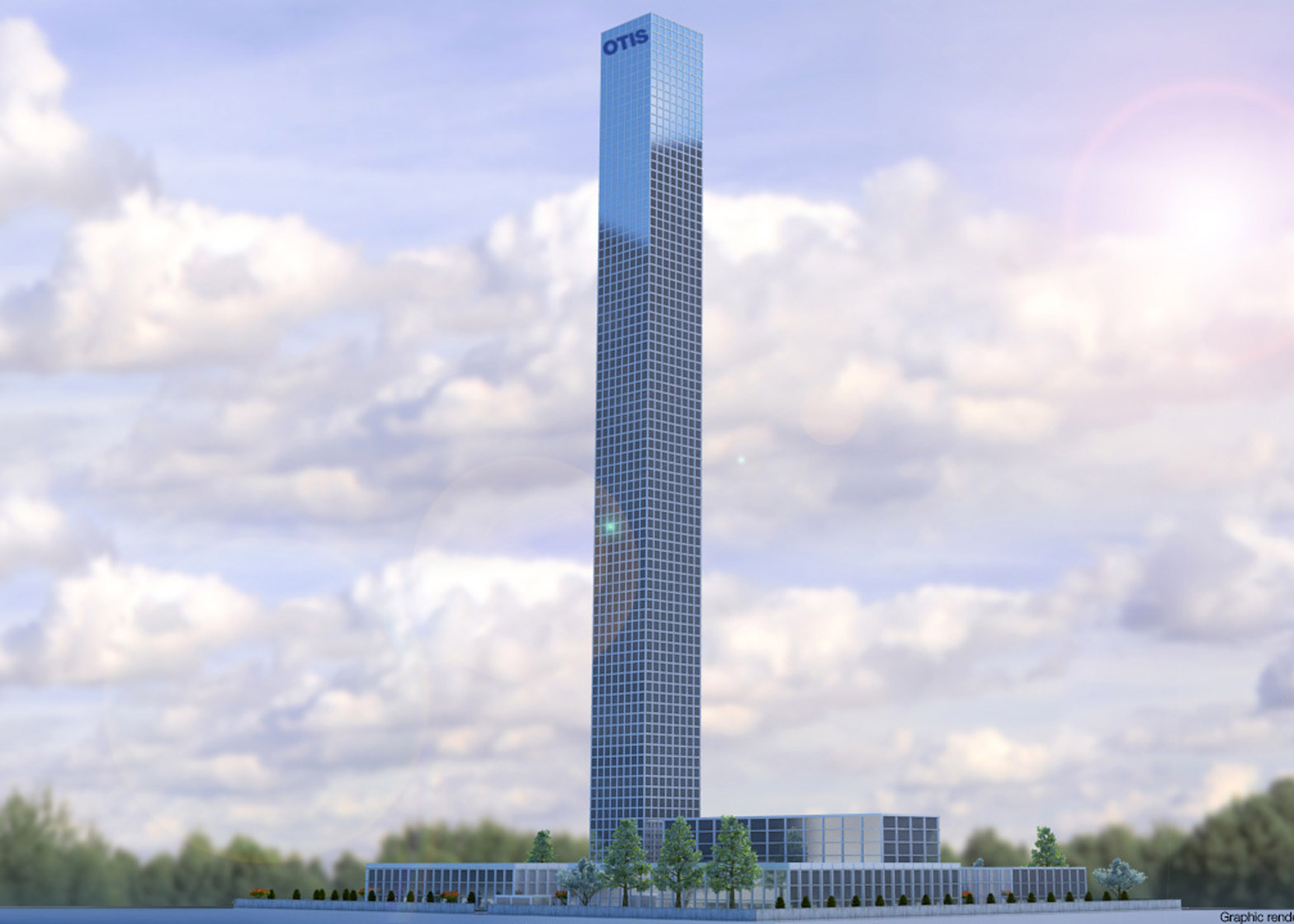

Otis Test Tower – Shanghai, China: 270 m
The new test tower, together with the product research and development facility, will support the development of new technologies for use in elevators for general-purpose market segments. The tower was completed in 2018.
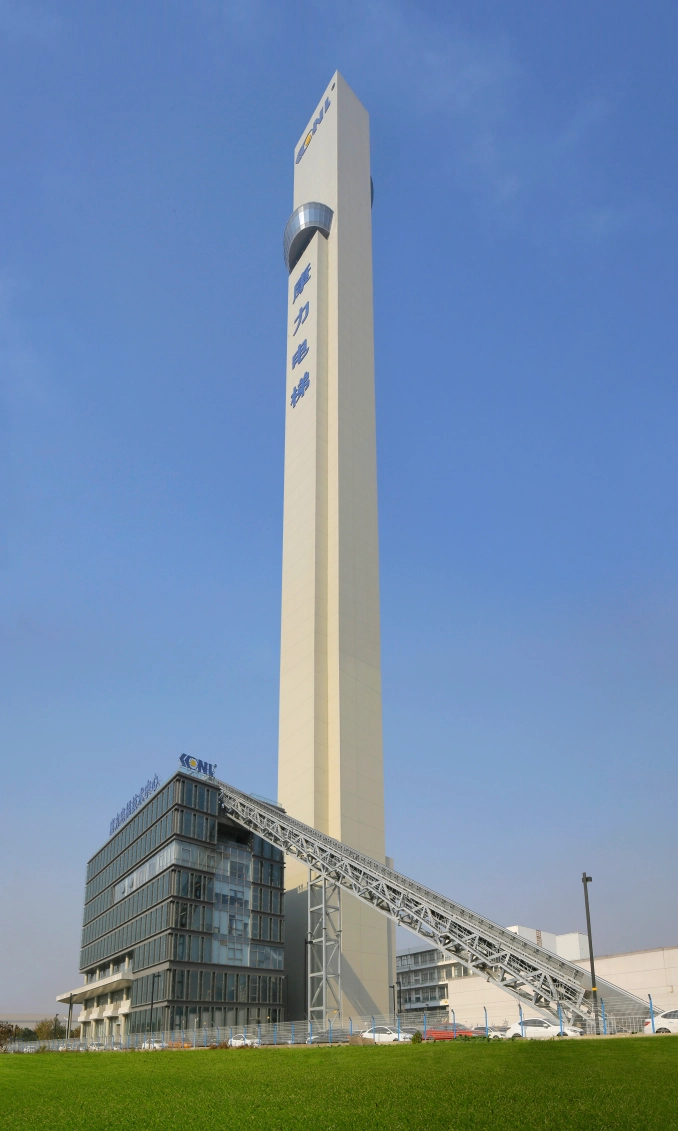

Canny Test Tower – Jiangsu, China: 268 m
If counted enough, this tower has a height of 288 m, including a part of 20 m underground.
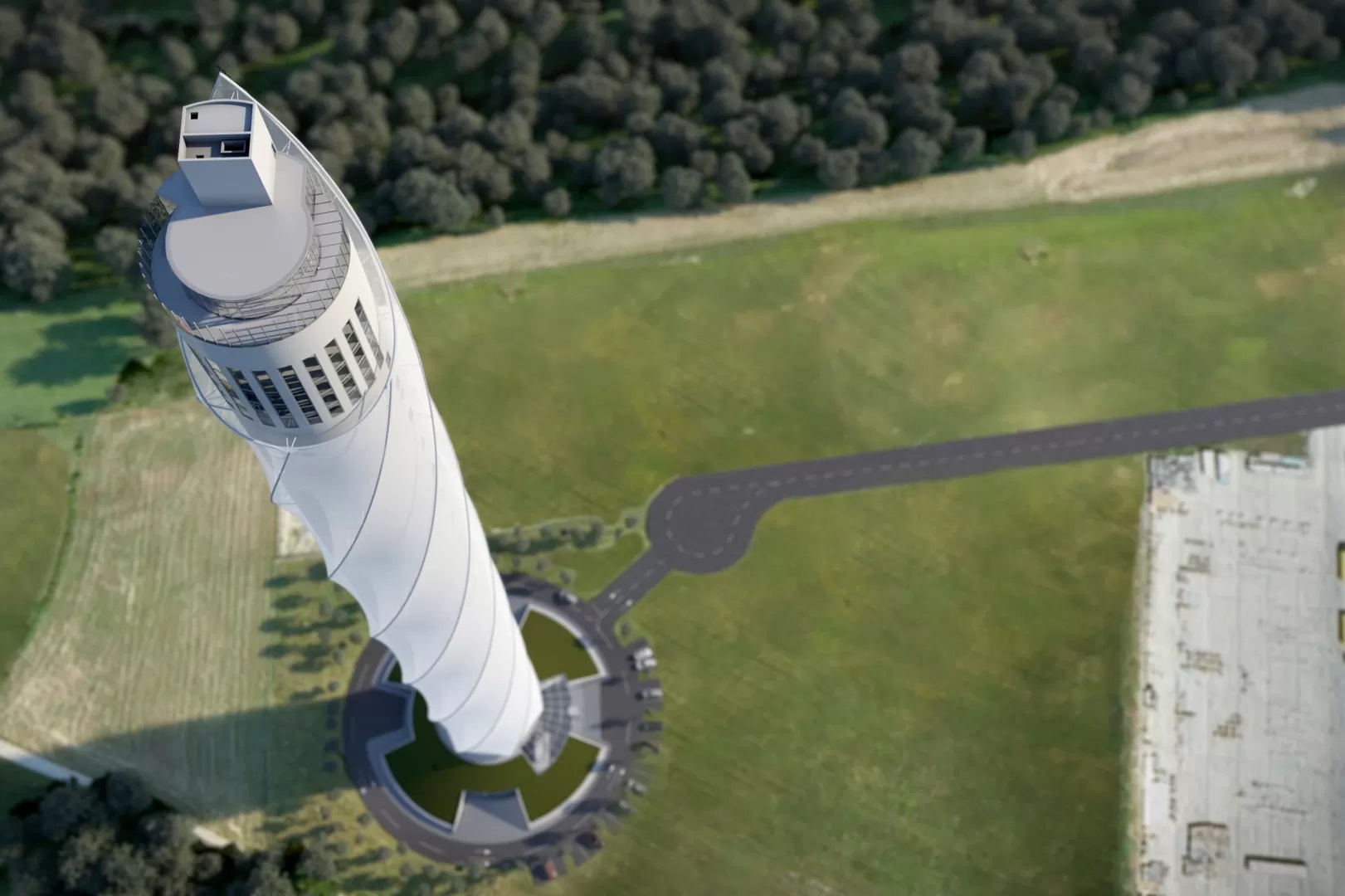
Test tower TK – Rottweil, Germany: 246 m
The TK elevator test tower in Rottweil, Germany was built to test the MULTI elevator system of ThyssenKrupp. At 246 m, the tower contains Germany’s tallest observatory and the sixth tallest in Europe. It was completed in 2017 and was the tallest elevator test tower in the world at the time.
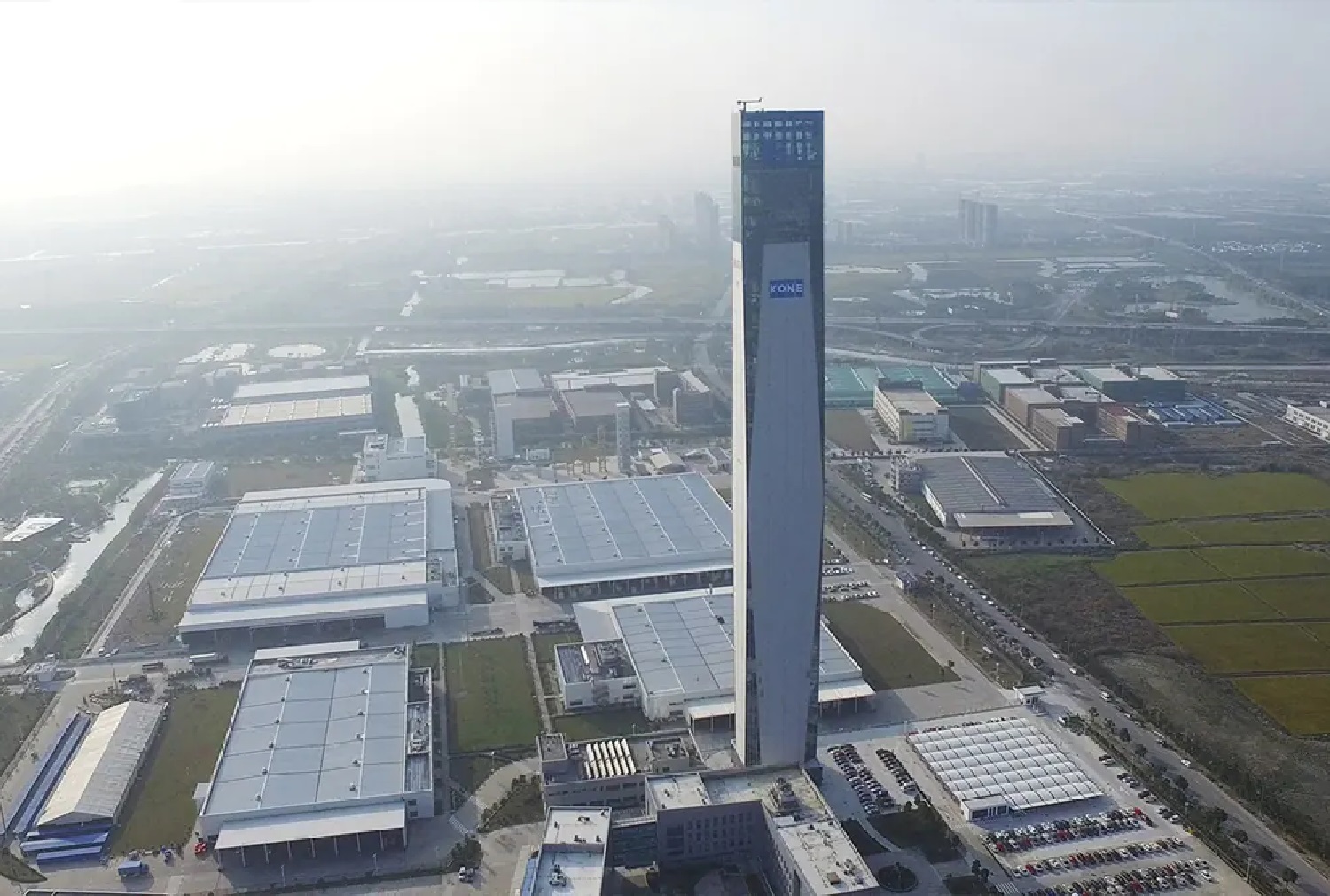

Kone Test Tower – Kunshan, Jiangsu, China: 235 m
The 36-storey tower with up to 12 elevator shafts will be the place where the group will test its new elevator technologies, solutions and products. An elevator with a speed of up to 10 m/s is fixed here to serve visitors to visit and also serve the travel of staff, scientists working here.
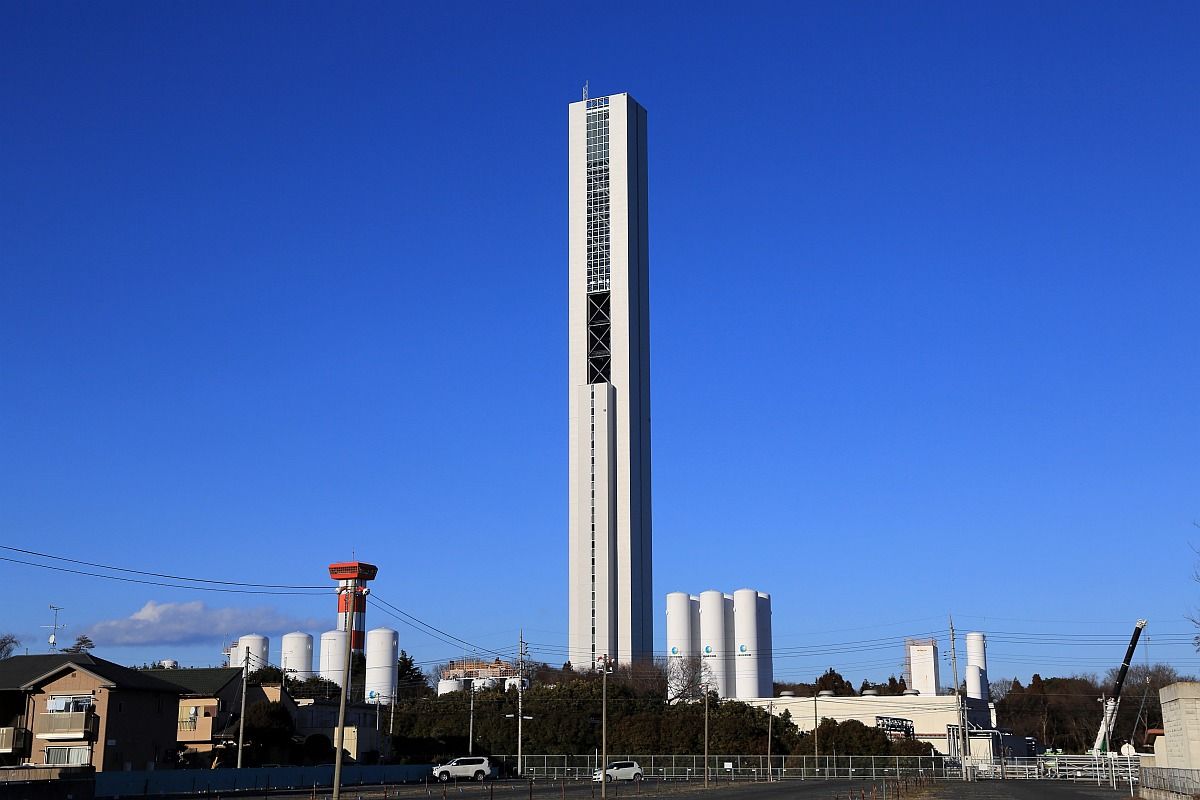

G1 Tower – Hitachinaka, Ibaraki, Japan: 218.5 m
The G1 Tower test tower in 2010 was the world’s tallest elevator test tower. It is 218.5 m high and has enough room for 7 different elevator clusters operating at speeds above 5.5 m/s.
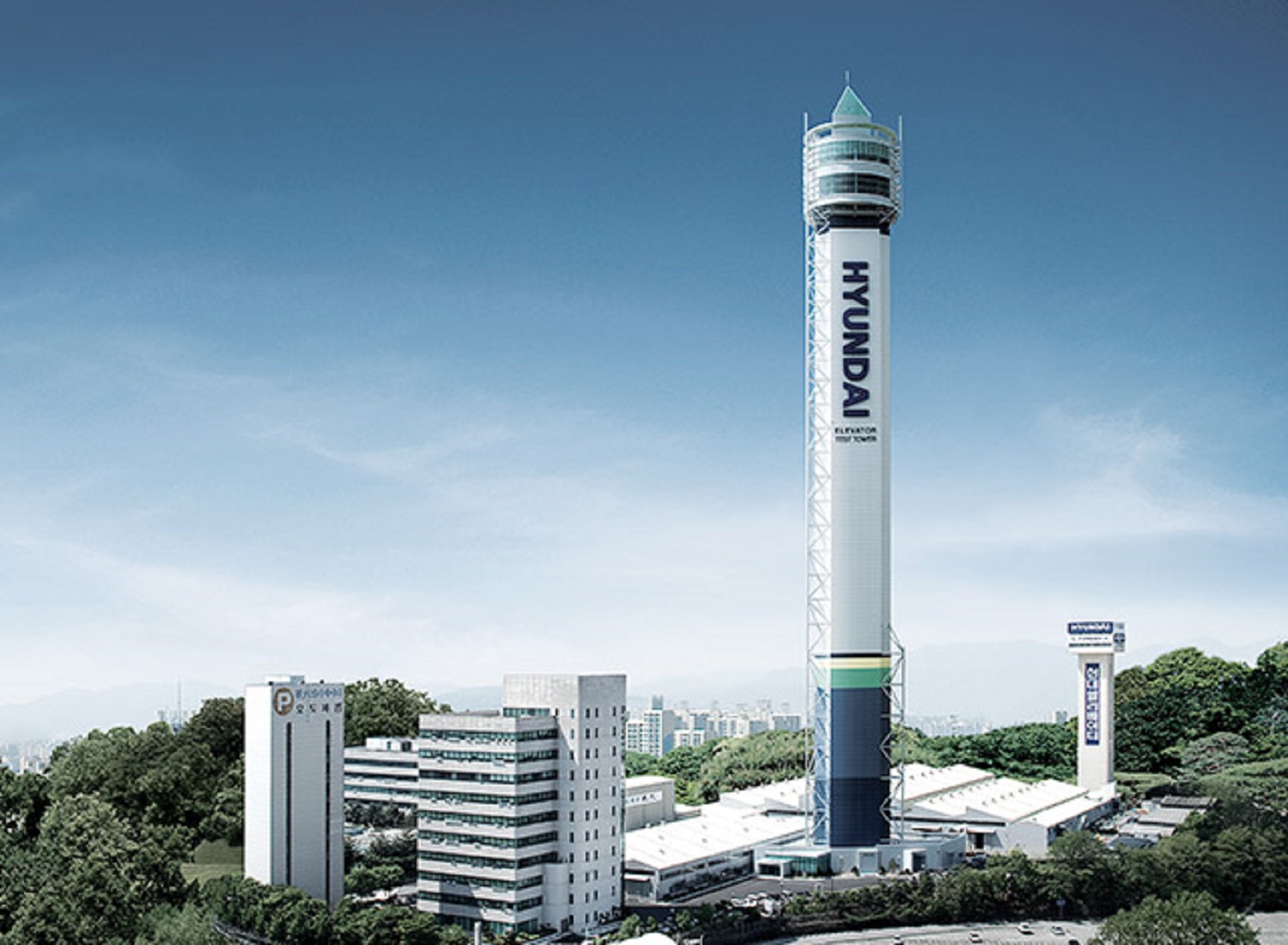

Asan Tower – Icheon, South Korea: 205.2 m
Hyundai Asan Tower, 205.2 m high elevator test tower. The column that makes up the main frame of the tower is modeled after the triangular logo of the Hyundai Group. The Hyundai Asan Tower embodies the entrepreneurial spirit and will of Hyundai: to rise to the top of the world. The tower includes the elevator research and development center with the policy of “Technology Independence” and “Hyundai Technology”.
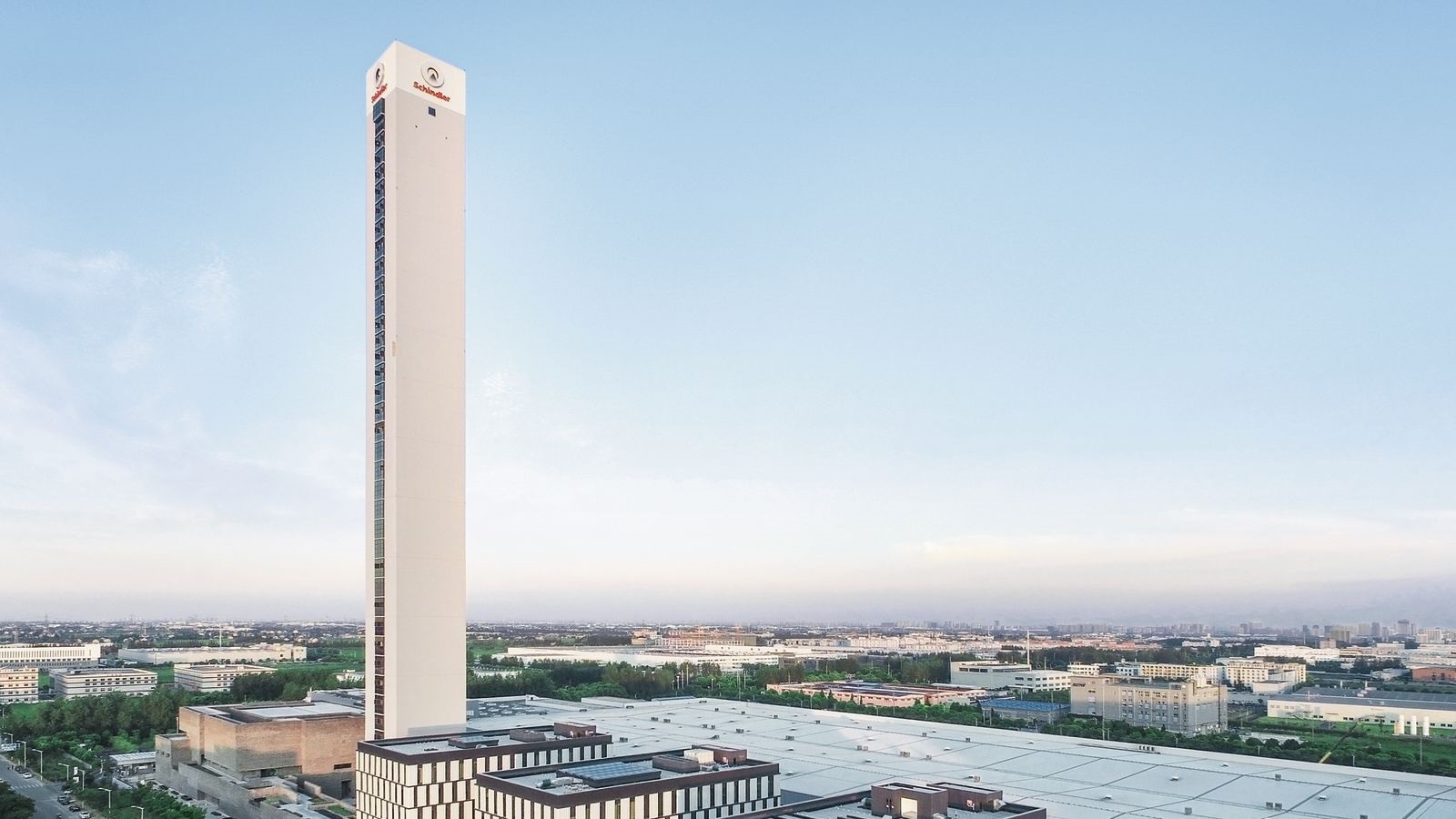

Schindler Test Tower – Shanghai, China: 200 m
The Schindler manufacturer’s test tower in the city has achieved the highest certification according to internationally recognized environmental standards. The complex includes a 200-meter-high test tower, an R&D center, a training center and Schindler China’s headquarters with showroom, canteen and large entertainment areas for employees.
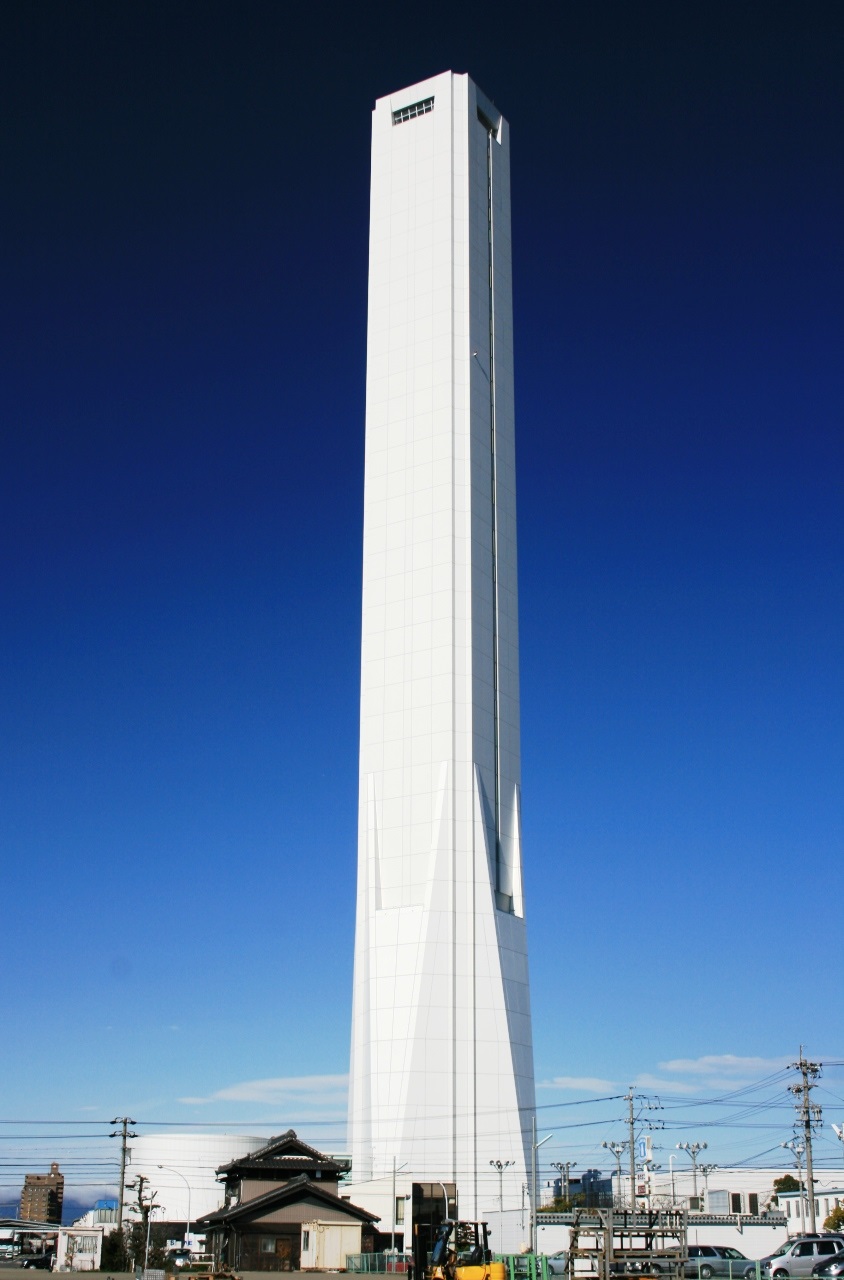

Solae Tower – Inawaza City, Japan: 173 m
The elevator test tower named Solae of Mitsubishi Electronics Corporation was built in Inazawa city, Japan. With a height of 173 m, this test tower is used in the research and testing of a new generation of high-speed elevators for ultra-high-rise buildings. It allows Mitsubishi to inspect the elevator’s transmissions, motors, cables and other systems./.



